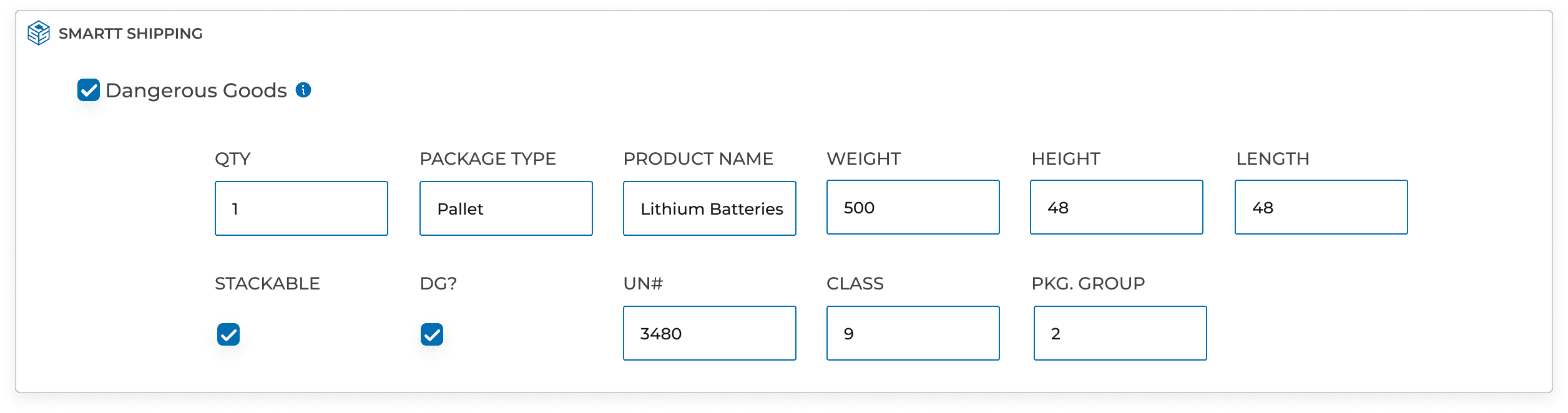
Dangerous Goods
What are Dangerous Goods?
Dangerous goods, also known as hazardous materials, are substances or articles that pose a risk to health, safety and the environment during transportation. These goods have specific characteristics that require special precautions to ensure their safe handling, storage and transport.
Classification
Dangerous goods are classified based on their specific hazards. The classification system, often referred to as the United Nations (UN) Model Regulations, assigns a unique UN number, proper shipping name, and hazard class to each dangerous substance.
Documentation
Accurate and complete documentation is essential for the safe transport of dangerous goods. Shipping papers, such as a Dangerous Goods Declaration or a Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods, provide essential information to carriers, handlers, and emergency responders.
Packaging
Proper packaging is crucial to prevent leaks, spills, and other accidents during transit. Packaging must meet specific standards and be designed to withstand the hazards associated with the materials being shipped.
Dangerous Goods Classification
Below are a list of some dangerous goods. Please note that this list is not exhaustive and it is your responsibility to know whether or not your products are classified as dangerous goods.
Class One: Explosives
- Fireworks
- Ammunition
- Airbag Inflators
- Aerosols
- Fire Extinguishers
- Propane Cylinders
- Paints
- Lacquers
- Alcohol
- Matches
- Carbon
- Sodium Batteries
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Ammonium Nitrate Fertilizer
- Pool Chlorine
- Medical Waste
- Dyes
- Pesticides
- Density Gauges
- Medical Treatment Products
- Uranium
- Acids/Acid Solutions
- Batteries
- Dry Ice
- Internal Combustion Engines
- First Aid Kits

explore logistics with Our complete shipping solutions Blog





